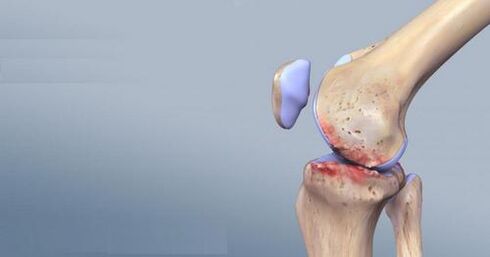
Arthrosis, gonarthrosis, osteoarthritis are synonymous terms that define the same disease: deforming changes in the cartilage tissue of the knee joint.
The human knee joint is made up of three bones: the femur, the tibia, and the patella. At the moment of contact with each other, these bones are covered with cartilage tissue, which ensures a smooth sliding of the surfaces between them.
Over time, these cartilage thins, losing their elasticity and elasticity. Cartilage is fed by the synovial fluid; the shock-absorbing properties of the joint depend on the quantity and quality of the fluid.
First symptoms and signs
- They most commonly occur in people aged 45-50 years. This disease is common in both men and women, but the "weaker sex" suffers from this disease much more often.
- At the onset of the disease, the patient experiences tolerable pain in the knee joint and severe pain develops over time.
- The intensity of the pain changes: it becomes stronger with movement and physical activity, at rest - the pain recedes.
If you do not pay attention to these symptoms of the impending disease in time, the disease will progress and in severe cases lead to disability.
During contact with a doctor, the diagnosis of arthrosis is clarified using X-rays. The images show the narrowing of the common space from the inside or outside of the joint. But over time, the pathological process seizes the entire joint. Osteophytes are visible along the edge of the joint surface - bone growths.
The main signs of knee arthrosis are:
- During the day the pain increases, during the night rest the pain subsides. But if venous insufficiency is present, dull pains persist at night.
- Muscle tension in the joint area
- There is a crack in the knee joint while walking
- In severe cases of the disease, deformation and swelling of the affected joint can be observed, increasing in volume.
- When touched, the joint is painful
- When you move the knee pad, the pain increases
- In the late stages of the disease, muscle shortening occurs and the patient is unable to position his leg
- Without treatment, joint mobility decreases or is completely lost
What is patellofemoral arthrosis of the knee?
Very often you may hear a diagnosis of "patellofemoral arthrosis" from your doctor - what is it? Indeed, such arthrosis is lacking in the international classification of diseases. Few know that arthrosis of the knee joint begins with the development of patellofemoral syndrome.
This syndrome occurs when a part of the body is exposed to regular overload or repeated injuries. That is, patellofemoral arthrosis is the same as patellofemoral syndrome.
The main causes of the disease are:
- congenital and acquired deformity of the lower extremities;
- various disorders of patella formation;
- regular overload of the knee joint (e. g. in athletes).
Patellofemoral arthrosis of the knee joint has the following clinical manifestations: pain in the anterior side of the knee joint, which increases significantly with physical exertion (running, jumping, moving up and down stairs, various squats). The pain may also increase if the patient is sitting with bent legs. The patient may feel tension and stiffness in his knee, both inside and at the front.
Patellofemoral syndrome is diagnosed clinically and usually no further testing is required.
This disease usually does not require special treatment. However, the following procedures are required to reduce pain and develop undesirable consequences (instability of the patella, knee deformity, accumulation of inflammatory secretions):
- decrease in physical activity. This does not mean that the patient should lead a passive lifestyle, only the level of activity should not be painful;
- uses a special bandage worn in the knee joint area during exercise or stress, thereby supporting and securing the kneecap;
- with severe pain syndrome, glucocorticosteroids and anesthetics are injected with precise injections into painful areas of the joint that relieve pain and help avoid the use of anti-inflammatory drugs in the future.
If patellofemoral arthrosis has already led to complications or is associated with other degenerative-dystrophic pathologies in the knee joint, therapy should be performed according to the treatment regimen for knee arthrosis.
The reasons
- An occupational disease of athletes who experience increased stress at the knee joints. Athletes suffer injuries and joint microtraumas, bruises and ligament tears. After retiring from the sport, the muscle skeleton weakens, leading to disease progression.
- Increased life expectancy and increased physical activity in middle-aged people
- Increased physical activity at the knee joint in people who "spend their working day on their feet"
- Genetic predisposition
- Congenital diseases of the joints and bones
- Lack of collagen
- Knee injury
- Being overweight, which puts more strain on the knee joints
- Acquired joint diseases
- Knee surgery
In order to achieve positive treatment results, a clinical and radiological examination should be performed that reveals several stages of the disease:
- Arthrosis of the knee joint is 1 degree. . . The joint gap narrows slightly, the edges of the surface are slightly pointed, a slight restriction of movement. During the arthroscopic examination, the doctor examines the softening of the cartilage.
- Grade 2 knee arthrosischaracterized by significant restriction of knee joint movement, strong crackling. The images clearly show osteophytes and a 2-3-fold narrowing of the joint space. Small cracks can be observed on the surface of the joint.
- Knee arthrosis grade 3- this is already a complete restriction of movement when deformation of the joint has occurred, deformation and compression, osteophytes and cysts can be observed on the surface of the joint. There were changes in the total thickness of cartilage tissue.
- Grade 4 knee arthrosis- arthroscopy shows complete absence of cartilage tissue.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy plays an important role in the complex treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint. Combined with physiotherapy procedures, therapeutic practices, and manual therapy, you can achieve very good results until your limbs function.
When knee arthrosis is diagnosed, medication helps relieve pain, normalize blood circulation in the problem area, improve metabolism and cartilage nutrition, activate recovery processes, and increase joint mobility.
Because it is impossible to use other therapies in the background of acute pain sensations, the patient is first prescribed painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. However, it is not recommended to use such funds for long periods of time because in addition to side effects (most often this has a negative effect on the digestive system) they can contribute to the dehydration and further destruction of cartilage tissue.
Chondroprotectors are used to restore cartilage food, regenerate cartilage plate, and improve the quality of joint fluid.. . . Drugs in this group are injected directly into the sore joint and are the safest for the patient. They fall on the affected area immediately, and the chondroprotectors save the joint from destruction and help restore its functions. One of the disadvantages of this method is the long wait for the result - the patient can only notice improvement after a few months. In addition, it is not advisable to take chondroprotectors if the disease is in the third stage and the joint is almost completely destroyed.
Various ointments and creams are used to reduce pain, relieve swelling, and slightly improve joint mobility.Various warming agents have a beneficial effect on the ligaments and muscles, improve blood circulation and speed up metabolism in the joint. But they cannot be used in the presence of inflammation, in which case non-steroidal anti-inflammatory gels and ointments are used.
Compressions should not be neglected - they have penetrating abilities, improve blood circulation, have an anesthetic and anti-inflammatory effect, and speed up metabolic processes in cartilage.
Therefore, you should not delay a doctor’s visit in people who are suspected of having knee disease or arthrosis - timely and properly selected medication can save the joint and avoid surgery.
Drugs for the treatment of knee arthrosis
Treatment for knee arthrosis is never complete without the use of medications.
Drug therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating inflammation and pain, improving local blood circulation and nutrition of articular cartilage, activating metabolic processes, and restoring joint mobility.
What medications are prescribed for knee arthrosis?
- To successfully treat the disease, you must first alleviate the pain and eliminate the inflammatory process. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used for this purpose. However, you should not be captivated by these foundations - they tend to obscure the true clinical picture of the disease when used for a long time.
- Chondroprotectors are used to restore the cartilaginous surface of joints, restore structure, nourish cartilage, and improve intraarticular fluid production. The effects of these drugs are very slow, so before the patient notices real improvement, they need to do 2-3 courses of chondroprotectors that last for about a year.
- Gels and ointments may be used in combination with other drugs to improve the general condition of the patient and relieve pain. If the course of arthrosis is accompanied by synovitis, ointments based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are preferred.
- Intra-articular injections are used to provide emergency care for arthrosis. The most commonly injected corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid.
- For topical treatment, drug compresses are prescribed - dimethyl sulfoxide, biscophite, and medicinal bile. Dimethyl sulfoxide is able to penetrate the skin's barriers, meaning that its effects are directed directly to the site of inflammation. This substance has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, absorbent properties and improves metabolism in its area of application. Biscophite, a derivative of oil, also has an anti-inflammatory effect on the affected joint, giving it a warming effect. Medicinal bile has the same properties as dimethyl sulfoxide containing bischophyte, but its use is limited by some contraindications. Medical bile should not be used in patients with pustular skin disease, fever, and inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Before starting treatment for arthrosis of the knee joint, a doctor should be consulted, the dosage, the characteristics of the application and the duration of treatment should be discussed.
Injections in the knee joint due to arthrosis
Intra-articular injections are one of the most effective methods of treating knee arthrosis. This rather expensive procedure significantly reduces pain and inflammation, and new modern drugs not only improve the general condition of the patient but also treat the affected cartilage tissue.
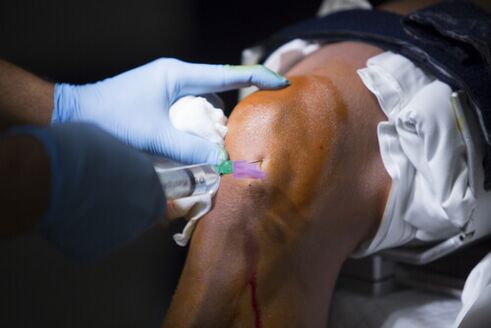
Injections of arthrosis into the knee joint are a rather difficult procedure, so you should consult your doctor, even if the patient knows what medications to administer and in what amounts.
The following medications are most commonly prescribed for intra-articular injections:
- Corticosteroid hormones. These are the most common treatments, as they take effect within minutes of their introduction. However, to relieve inflammation and pain, corticosteroids negatively affect the joint itself - cartilage tissue remains degenerative, and drugs in this group cause narrowing of the blood vessels, which also destroys joint tissue. Therefore, the use of corticosteroid hormones is only justified in case of intolerable pain in the last stage of arthrosis. The injection can be repeated up to every two weeks.
- Chondroprotectors and enzymes. Unlike hormones, they do not reduce inflammation, so dosing is meaningless in the presence of joint swelling. But they have a regenerating effect, partially restoring cartilage tissue. The use of such drugs is particularly effective in the early stages of arthrosis. The cure is 5-10 injections.
- Hyaluronic acid. It is a very effective, yet expensive drug. Its effectiveness lies in the fact that the composition of the acid itself is similar to the natural lubrication of the joint. After the administration of drugs with hyaluronic acid to the knee, the friction of the affected joint surfaces decreases and the mobility of the knee improves. Such injections are very effective in the initial stage of arthrosis, with a slightly smaller effect in the second stage, and with arthrosis of the third knee joint, such drugs only briefly alleviate the patient's condition. The course of treatment usually involves three to four injections once a year.
In case of arthrosis, knee joint injections are strictly contraindicated:
- infection of the skin or subcutaneous tissue at the intended injection site;
- blood poisoning;
- infectious arthritis;
- hemorrhage;
- the presence of a viral infection;
- lack of results from previous injections;
- individual intolerance to the drug.
Intra-articular injections are also not acceptable for prophylactic purposes.
Orthopedic knee pads for arthrosis of the knee joint
In the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint, knee pads are used to prevent various injuries as well as to support the damaged tissues and relieve the stress of the joint.
An orthopedic knee pad is essentially the same as a flexible bandage. Compared to the latter, however, the knee brace has its advantages: it does not need to be bandaged several times a day, it will not slip or hang, a properly fitted knee pad will not compress your legs and will not cause swelling and other unpleasant consequences. prolonged squeezing.
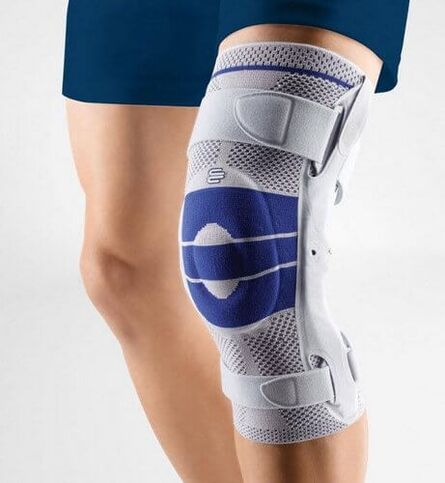
The orthopedic knee pads required for knee arthrosis perform the following tasks:
- reduce inflammation and pain;
- relieves swelling;
- relieves stiffness and tension;
- normalizes blood circulation;
- they facilitate the free movement of the joint.
When choosing an orthopedic knee pad, you should pay attention to the following features:
- Knee pad type - selected depending on the severity of the pain. These types of knee pads are:
- closed - used when it is impossible to determine the location of pain;
- open with adjustable voltage - used during rehabilitation and for minor pains;
- open with spiral stiffening ribs - in case of pain during the ascent and descent of the stairs, etc. ;
- articulated - for different types of pain;
- tendons - used when the pain is localized under the patella.
- The material from which the knee pad is made is of great importance, as not only the degree of fixation but also the intensity of the warming effect depends on it. Modern knee pads are made of cotton, lycra, nylon, neoprene, spandex, camel and dog fur.
- The size of the knee pad, which is calculated separately for each patient.
Your doctor will help you determine the parameters of your future purchase - not only will you choose the size and type of knee pad that is optimal for your patient, but will also advise you on which material will be most effective.
An orthopedic knee pad for arthrosis can be purchased at a pharmacy or specialized medical equipment store, and its price is quite acceptable. You should beware of such purchases from non-specialized stores or dubious companies, as you can easily buy a fake that, if it doesn’t hurt, it certainly won’t help.
Proper nutrition
Nutritionists have been studying the nutritional characteristics of different peoples for years. By comparing national cuisines, scientists try to understand the impact of people’s culinary preferences on the incidence of certain diseases. This type of research has been done many times in connection with a common disease such as arthrosis of the knee joint.
Many theories were born, a great variety of assumptions were made. For example, at one time it was thought that the use of tomatoes contributed to the development of the disease, it was suggested that table salt was "faulty" in the appearance of arthrosis.
In the twentieth century, the situation of the development of the disease deteriorated sharply.
Proper nutrition is the key to joint health.
To prevent the development of the disease, it should be understood that nutrition plays a key role in knee arthrosis. Consumption of meat products from the fast food segment should be kept to a minimum from the diet. These products:
- semi-finished products from meat production waste: sausages, sausages, all kinds of sausages, etc.
- smoked meats sold in shops (most often such products are made using chemistry and not in smokers).
- ready-to-eat meat - ham, bacon (manufacturers in this case do not hesitate to use flavor enhancers and colors).
- fast food.
Of course, not all people are able to give up the above foods. Over the years, many have become accustomed to pampering themselves with smoked sausage sandwiches or cooked sausages in the morning. In this case, we advise you to buy a piece of meat on the market, bake in the oven with spices, cut it off and then use as a basis for sandwiches. This kind of "fast food" does not harm the body.
So we realized that it is best to refuse semi-finished products, smoked meats and fast food. But what about meat when injected?
The ideal option, of course, is to buy meat from reliable suppliers, but in urban conditions, this advice is impractical.
In this regard, such cooking methods should be used to kill as many harmful chemical compounds as possible. Sometimes only the use of this factor made it possible to achieve an excellent effect in the fight against arthrosis.
How to properly prepare food for arthrosis of the knee joint
It should be recalled that the diet of arthrosis of the knee joint cannot be saturated fats.
Therefore, when preparing the food, the visible fat of the meat must be cut off and the poultry skin removed. The highest amount of harmful substances is concentrated in fat.
Cooking, steaming, foiling and steaming are the healthiest ways to prepare food.
With arthrosis of the knee joint, jelly and jelly meat should not be eaten. The "grandmother in the yard said" series thinks these foods are good for the joints, but that's not the case. People with arthrosis only get worse because of high cholesterol.
Broths and soups should be consumed as little as possible. Even if the first broth is drained, there will still be a lot of unhealthy fat in the second. You better get used to the vegetable soups that are so popular in western countries. Mushroom soups are also helpful.
The attempt to replace meat for soup with dry broths and cubes does nothing good: these products contain an incredible amount of chemical components.
Unfortunately, fish sold in our markets are also diligently injected with dyes and preservatives, making it harmful to arthrosis of the knee joint. Therefore, if possible, you should buy live fish. Clearly, not everyone has enough money for this. The above methods will help you to properly prepare your frozen fish.
Prevention of knee arthrosis
It is impossible to allow the condition of life to deteriorate due to the disease, so the causes that lead to arthrosis must be ruled out. It is much easier to prevent the disease than to deal with expensive and long-term treatment.
- You have to lose weight.
- The joints need constant physical activity: skipping rope, squats, little running. But everything has to be in moderation. Excessive exercise also leads to illness. Alternating joint load with adequate rest.
- Knee injuries cause arthrosis. Wear padded knee pads when skiing, skating, cycling or rollerblading. Sufficient selection for sale of both fastening knee pads and sheep wool heating.
- Do not ignore the help of another person if the weight exceeds your strength.
- Eat more vegetables and fruits. We note that vegetarians practically do not suffer from arthrosis. Replace the mayonnaise with olive or mustard oil. Especially useful are plums, dried peaches, apricots, apples, raspberries, blueberries with honey.
- Strong tea and coffee wash away large amounts of calcium.
- Homemade cottage cheese and cheese help strengthen bones.
- Walking with reeds will save you from overloading your knee joints.
- The shoes should be comfortable with small heels.
- Swimming and water aerobics relieve stress throughout the body and fatigue of the knee joints.
- Of the vitamins, vitamin E is particularly useful in preventing cartilage tissue destruction.
- Vitamin C is involved in the synthesis of cartilage tissue.
- The disease progresses faster from vitamin D deficiency.
- Calcium helps strengthen bones. High calcium content in sesame and celery seeds.
By following these simple rules of a healthy lifestyle, you can avoid serious illness. And when the disease manifests itself, they slow down the development of pathological processes.























