Most often, 20-50 year olds consult a doctor with such problems, but it happens that children also get sick.According to statistics, about 85% of people have experienced lumbago or discomfort in the back at least once.Pain occurs due to overstretching of muscles and ligaments, spinal problems and diseases of internal organs.
The mechanism of the development of back pain
This is the most vulnerable part of the body due to the structure and functions of the spine.Unpleasant sensations occur in the neck, chest or between the shoulder blades, but more often the pain is localized in the lumbosacral region of the back.
The mechanism of its formation is related to the following factors:
- Overload, muscle tension.A decrease or increase in tone causes microtraumas, myositis (inflammation) and muscle pain (acute pain).
- Diseases of internal organs.In 10% of cases, they cause irradiation of back pain.
- Reduced strength, deformation of intervertebral discs or joints.The process occurs due to an increase in the external load on the spine (overweight, heavy lifting) or its uneven distribution (uncomfortable working posture).In severe cases, the discs bulge and compress the nerve roots.
Classification of back pain
In order to facilitate the description and the correct choice of treatment tactics for back diseases, we distinguish the symptoms of pain based on their duration.In addition, doctors highlight the nature and location of the attack.
Depending on the type of pain, there are:
- acute, lasting from several days to one and a half months;
- subacute, disturbing for 6-12 weeks;
- chronic, which are present for more than three months or continuously (periods of exacerbation followed by rest).
Based on the nature of the sensations, back pain is classified as follows:
- Local.They are caused by changes in nerve receptors, muscles and ligaments, tendons or skin.The pain can be acute, sharp, throbbing, but always felt in the soft tissue area.
- is reflected.The pain syndrome is projected from the internal organs to the back.It can be burning and intense, but never worsens with movement.
- Irradiator.The discomfort appears suddenly, sometimes it is migratory - radiating to the arm or leg.It appears when a nerve root is irritated or stretched.
Based on localization, we distinguish the following conditions:
- Lumbodynia- acute pain in the lumbar region.
- Sacralgia– discomfort of the sacral spine.
- Lyubmoischialgia– the lower back hurts, the feeling radiates down the leg.
- Cervical pain- neck inflammation.
- Coccydynia- pain in the coccyx.
- Thoracalgia– peripheral nerve disease causing discomfort in the chest.
Pain in the lumbar region
Lumbalgia is often painful and is characterized by a gradual development.The pain syndrome occurs with dystrophic changes of the spine and muscle spasms against the background of displaced discs or herniation.
Old people and young people often experience back pain in the lumbar region when they spend a long time in an uncomfortable position.
The discomfort disappears without any manipulation, but suddenly reappears.Severe low back pain occurs with vascular diseases such as abdominal aortic aneurysm or damage to the gluteal artery.Then the symptom is constantly present and does not go away even during rest.
Back pain in the sacral region
Sacralgia occurs against the background of pinched spinal nerve endings due to spinal deformation or soft tissue inflammation.It occurs more often in men than in women.Pain in the lower back can be sharp, dull or pulling.
Unpleasant sensations intensify during physical activity, after prolonged sitting or a sudden change in body position.Sometimes the pain radiates to the buttocks or legs.
Sacralgia is also provoked by gynecological diseases, injuries, tumors and mental disorders.
Pain in upper back
This condition is associated with thoracic or cervical spine problems and severe muscle tension.The pain is caused by heavy loads, incorrect posture or osteochondrosis.
The cause of the syndrome can be diseases of the internal organs:
- Pleurisy.It is characterized by a cutting pain on the right or left side of the chest that intensifies with inhalation.
- Pneumonia.The condition causes mild pain behind the sternum or between the shoulder blades.The discomfort increases with coughing and deep breathing.
- Tuberculosis or lung cancer.They often experience aching pain in the shoulder, chest, arm, and middle of the back.The intensity of the symptoms depends on the severity of the disease.
Pain in the shoulder blades
The discomfort occurs when the nerve endings in the chest become inflamed - intercostal neuralgia.The pain syndrome is moderate, it hurts, it goes away after rest or massage.It is often caused by cardiovascular diseases (heart attack) or psychological problems.
Symptoms related to back pain
The intensity and nature of the clinical picture depends on the cause of the pain syndrome, while the main symptom is complemented by:
- nausea, vomiting;
- weakness, loss of strength;
- an increase in local body temperature;
- stiffness of movements;
- thrombosis, thrombophlebitis;
- dizziness;
- sudden weight loss;
- difficulty breathing, cough;
- reduced visual and hearing acuity;
- swelling, inflammation of the soft tissues around the joint;
- urinary incontinence, reduced sensitivity of the limbs.
Why does my back hurt?
There are two types of discomfort: primary and secondary.The first group is caused by diseases of the spine, the second by disorders of the functioning of internal organs and neurological causes.Women's back pain is noted separately.
The following factors contribute to the appearance of the unpleasant symptom:
- rowing, skiing or high jumping;
- long-term static loads;
- overweight;
- hypothermia;
- sudden movements;
- vibrations in the workplace;
- heavy physical work (spine pain occurs in miners, farmers, machine operators);
- uncomfortable posture;
- curvature of the spine;
- previous injuries or broken bones.
Pathologies of the spine
The main causes of back pain are associated with a violation of the integrity or functionality of the spine, and there are factors that include diseases:
- Osteomyelitis- necrotic process in bones and bone marrow.
- Protrusion– displacement (protrusion) of disks.
- Arthritis– arthritis.
- Scoliosis– curvature of the spine of varying severity.
- Intervertebral hernia– displacement of the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc and rupture of the connecting end.
- Spondylosis- proliferation of bone tissue.
- Narrowing of the spinal canal– compression of the nerve endings and a part of the spinal column due to the displacement of the disc.
- Radiculitis– damage to the nerve roots of the spinal cord.
- Spondyloarthrosis- dystrophic diseases of intervertebral joints.
- Osteochondrosis- degenerative cartilage diseases.
- Discitis– sepsis, purulent inflammation of cartilage discs.
Causes unrelated to the spine
Pain in the lower back and other areas of the back is often caused by diseases of the internal organs:
- Stomach ulcer.
- Tuberculosis.
- Appendicitis.
- Shingles.
- Stone in the ureter.
- Ulcerative colitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Malignant tumors.
- Nephritis.
- Aortic aneurysm.
- Angina pectoris.
- Intercostal neuralgia.
- Hemorrhoids.
- Prostatic dysplasia.
- Pancreatitis.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Heart attack.
- Cystitis.
- Acute coronary syndrome.
- Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle.
Causes of lower back pain in women
Unpleasant, nagging or sharp pain in women indicates problems with the urinary and genital organs.
Discomfort is caused by muscle tension due to pregnancy and the posterior or occipital appearance of the fetus.
Causes of pain in women:
- cancer of the body or cervix;
- external endometriosis;
- menstruation;
- premenopause;
- wearing high heels;
- inflammation of the ovaries;
- myoma or myoma of the uterus;
- ovarian cyst.
Diagnostics
If your back hurts, you should see a therapist.After collecting the anamnesis and the external examination, the doctor refers to a consultation with a specialist: traumatologist, urologist, neurologist, oncologist or gynecologist.
A number of tests are prescribed to establish the correct diagnosis:
- Radiographydetects fractures, bone injuries, changes in the height of intervertebral discs and possible growth of bone tissue.
- Myelography- the method of examination of the spinal cord, which evaluates the patency of the channels of the cerebrospinal fluid, the presence of hernias, tumors or damage to the spinal column.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)it shows disc protrusion, the presence of calcifications, spinal canal narrowing.
- General and biochemical blood test.The tests reveal inflammatory processes, elevated calcium levels and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- Electromyographyreveals the extent of damage to nerve endings and muscle fibers.
- Urine test.It is taken in case of suspected kidney and urinary tract diseases.
- Further researchTo rule out autoimmune diseases, digestive system diseases, rectal and hidden infections.
Treatment of back pain
The choice of treatment regimen depends on the factors causing the discomfort.If the pain is caused by diseases of the internal organs, treatment begins with eliminating the cause.Painkillers are prescribed to alleviate unpleasant symptoms.
In addition to tablets and ointments, doctors prescribe physiotherapy and reflexology.
Therapeutic exercises are recommended during the recovery phase.If pain occurs due to damage to the spine (hernia, bulging disc, injury), surgery is performed.
First aid for acute pain
If the discomfort is unbearable, help the victim before the ambulance arrives:
- Place the person face up on a firm or semi-firm mattress.This position gives peace to the muscles and relieves cramps.
- Apply a cold compress or numbing ointment to your back.
- If the discomfort does not improve, give an NSAID.
- If you must move, wear a back brace or support brace.
Drug therapy
The following drugs are prescribed to reduce pain, relieve swelling and other unpleasant symptoms:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.They have an analgesic and antipyretic effect and reduce inflammation.
- Ointments.Preparations that warm the muscles are pain relievers and are used for massage.
- Chondroprotectors.These products are used to protect and restore cartilage tissue.
- Diuretics.It is prescribed for diseases of the kidney, cardiovascular system and to eliminate edema.
- Muscle relaxants.They relieve muscle spasms and pain.
- Vitamin preparations.It improves the functioning of the nervous system and increases immunity.
If taking painkillers does not result in a therapeutic effect, a paravertebral block is performed.
An anesthetic solution is injected into the affected area.The relief is immediate and lasts up to 6-12 hours.
Physiotherapy
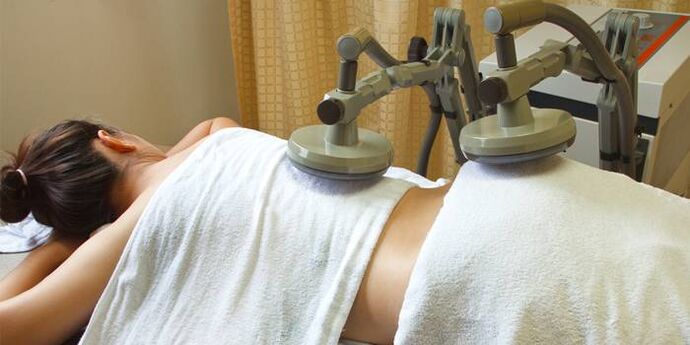
Manual and mechanical methods are used during the healing phase or in case of chronic pain.They improve blood circulation and tissue nutrition.
The following procedures are most often used:
- Diathermy.Heating the tissues with a strong current dilates the blood vessels, induces absorption of infiltrates, and increases blood flow.
- Electrophoresis- administration of drugs to the site of pain through the skin.The procedure relieves pain and improves tissue trophism.
- Acupuncturerelieves spasm of muscle fibers, eliminates the inflammatory process.
- Laser therapy– effect on the source of pain with the quantum particles of the light current.The procedure is performed with special equipment.Laser radiation penetrates into the deep layers of tissues, stimulates metabolic processes, relieves pain and removes swelling.
Surgical intervention
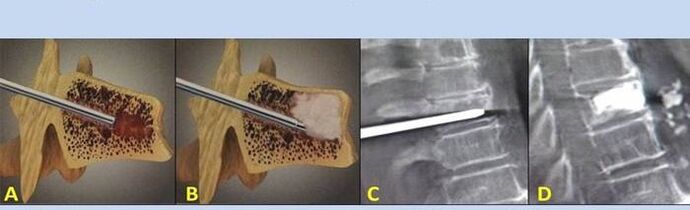
Indications for surgery include injuries, intervertebral hernias, and spinal cord compression.The main goal of this treatment is to eliminate pain.In addition, the surgeries restore the function of the spine and joints.
Doctors perform the following surgical procedures:
- Endoscopic discectomy.It is prescribed for the treatment of intervertebral hernia and is performed with an endoscope and microsurgical equipment.
- Open spine surgery.The doctor removes the affected disc, part of the vertebra, or the ligament.The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and is characterized by a long recovery period.
- Nucleoplasty– removal of the core of the intervertebral disc.The surgery relieves the pressure on the nerve endings.
- Stab vertebroplasty– the method of stabilizing the vertebrae.During the procedure, the doctor fills the cavities of the spine with bone cement.
Folk remedies against back pain

Decoctions and poultices made from herbs enhance the effect of medicines.With the permission of your doctor, use folk remedies based on natural ingredients at home.
Recipes to relieve pain:
- Mix 100 g of blue clay, 1 tbsp.l.aloe juice and honey.Add 750 ml of warm water.Apply the composition to the affected area of the back, cover with cling film and a woolen cloth.Leave the poultice on for 1 hour.Use the composition for osteochondrosis twice a day for 2-3 weeks.
- Dissolve 5 g of mummy in 1 teaspoon.water, add 1 g medical sulfur.Rub the mixture on your lower back and cover yourself with a warm blanket.Use the product daily in the evening.The duration of the treatment is 3-4 days.
- Mix 50 g of dry mustard, 20 g of alcohol, 50 g of camphor and 2 raw egg whites with a blender.Let it rest in the fridge for 5-6 hours.Apply the ointment to the painful areas 3-4 times a day.To enhance the effect, tie a woolen scarf around your back.
Prevention
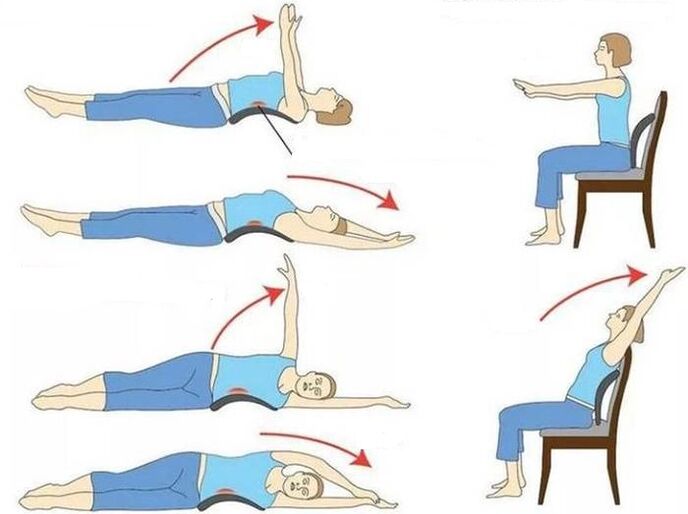
Following the doctor's recommendations will speed up recovery and resume physical activity, and to avoid later discomfort, follow the rules below:
- watch your posture;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- When working at a computer, use a chair with a back or a comfortable chair;
- watch your weight;
- don't get carried away by high heels;
- buy an orthopedic mattress;
- if you do sedentary work, do light exercises every 30 minutes;
- move more, do sports;
- See your doctor immediately.























