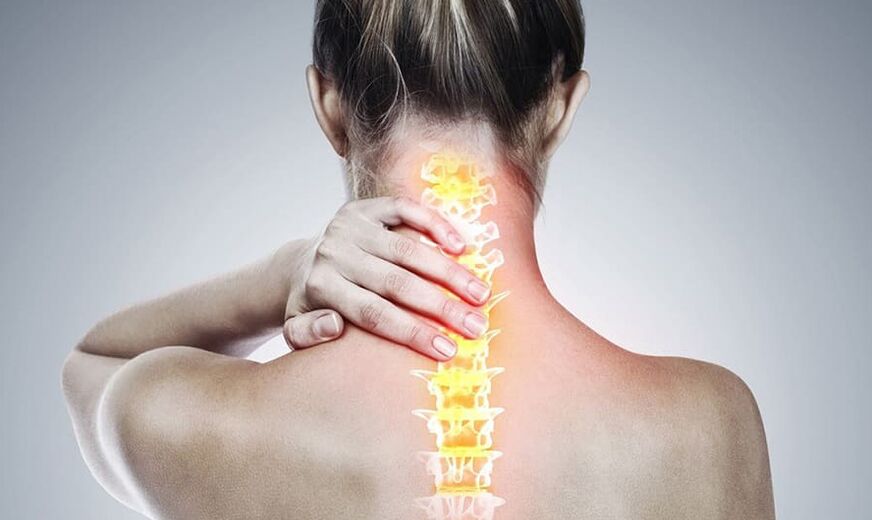
Do you know the tension in your neck?Sometimes he works and automatically pulls his head left and right because his muscles are "numb".Or you find yourself massaging your neck while reading a book.Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine may be hidden behind these symptoms.
What is cervical osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a disease of the skeletal muscle system and connective tissue of the cervical spine.It is characterized by a change in the cartilage structure of the intervertebral discs and the development of a pathological process in the surrounding tissues.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
The disease has several characteristic symptoms:
- Pain complaints (acute and dull, aching), which can be localized in the neck, back of the head, arms and shoulder blades.This is due to pinching of the nerve roots of the corresponding cervical segment.
- Muscle weakness and numbness in the neck and arms.
- Stiffness when moving the neck and vertigo.
- Increased fatigue and reduced performance may occur.
- Hearing and vision impairment are less common (in advanced disease).
The above symptoms and complaints can be combined.It depends on the specific location and extent of the pathological process.
Why does cervical osteochondrosis appear?
The causes of cervical osteochondrosis consist of many factors.It is most often caused by:
- Age-related changes in cartilage tissue are a normal aging process.
- Hereditary syndromes of connective tissue developmental disorders: Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, joint hypermobility syndrome.
- Low physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Bad posture that causes overload on the right part of the spine.
- Previous injuries to the corresponding part of the spine.
Incorrect stereotyped postures and habits greatly contribute to the development of the disease.Nowadays, due to the frequent use of gadgets and long working hours in front of the computer, they are becoming more and more common - the neck tilts forward and down.If you read for a long time and have an incorrect posture while sleeping - wrong pillow, mattress, sleeping on your stomach.As a result of these factors, the neck muscles are under constant tension.
How to treat cervical osteochondrosis?
For the effective treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, complex treatment methods are used, including:
- Drug therapy (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamin complexes based on B vitamins, magnesium, etc.).Medicines reduce pain and inflammation, reduce muscle tone.
- Therapeutic practice.Physiotherapy and massage improve blood circulation and saturate the affected cells with oxygen and nutrients.Thanks to this, the pathological process stops and the pain is alleviated.
- Physiotherapy procedures and massage.Physiotherapy can be performed in a medical institution or at home.For these purposes, almost the entire range of physiotherapy methods is used: electricity, laser, ultrasound, magnetic radiation, shock wave therapy.The choice of method depends on the stage of the disease and the presence of contraindications.
During work, it is advisable to establish the correct stereotypical positions of the head and neck, and the proper arrangement of the sleeping place.You may want to replace the pillow with an orthopedic one.
Prevention of cervical osteochondrosis
If you follow the following preventive rules, you can not only prevent the development of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, but also stop the development of the disease:
- Regular moderate physical activity and/or physical therapy.
- Maintain a healthy diet with enough water, calcium, magnesium and protein.
- Cervical spinal exercises during prolonged sitting, at least every two hours.
Gymnastics for the cervical spine
During the period of remission, do the exercises slowly, without sudden movements.In the starting position, inhale, and when you bend and turn your head, exhale.Hold it in every position as if you are stretching your neck muscles.
- Starting position: sit straight, look ahead.
- Tilt your head forward and then return to the starting position.Tilt your head back and return to the starting position.
- Tilt your head to the right, return to the starting position.Tilt your head to the left, return to the starting position.
- Turn your head to the right and then in front of you.Turn your head to the left and then in front of you.
If your health allows, you can use a more complicated version of gymnastics - the same movements, but with reverse arm resistance.Push his head forward and down and press with your hand, preventing his head from tilting forward and down.Do the exercise for 5-15 seconds, depending on your strength.Repeat the exercise in all indicated directions.
Important: gymnastics should not cause pain!
If there are obvious signs of the disease, it is necessary to contact a specialist for timely diagnosis, determining the stage of the disease and choosing an individual treatment tactic.























